Updated Move-VMStorage2 function for Hyper-V PowerShell
I have been updating my function that extends the Hyper-V PowerShell module cmdlet Move-VMStorage. A while ago I made a blog post about that I think that the folders on the source directory should be removed when doing a Live Storage Migration or you will get a mess with empty VM folders after a while and that can cause some confusion for the admins.
The updates in this script function are the following:
- I will not delete folders if they do not reside within a folder with the VM´s name (In the earlier version I just deleted and that recursive with no questions asked which could have some consequences )
- And if the folder was the default or named with another name you will get an output that tells you to clean manually
- If you do not give the VM´s Name in the -Path parameter I will add that for you to get a nice and tidy folder structure
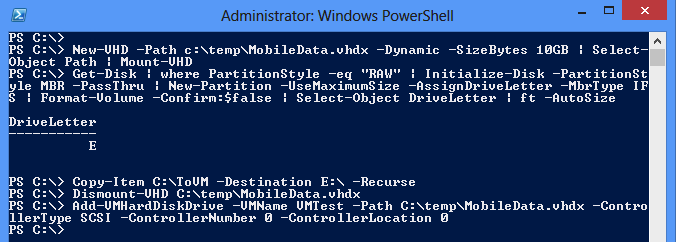
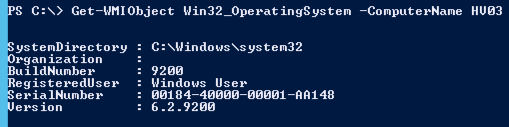
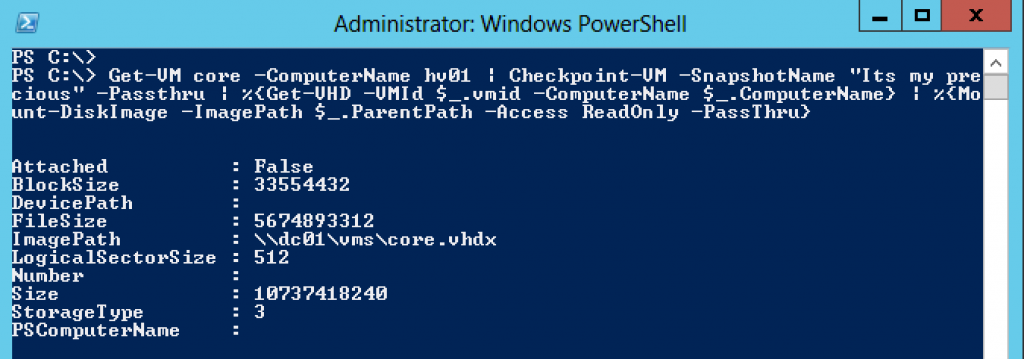
Here is a screendump on the updated function in action
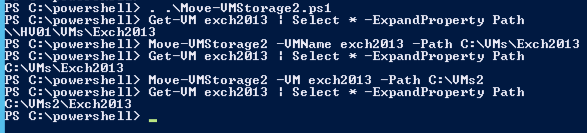
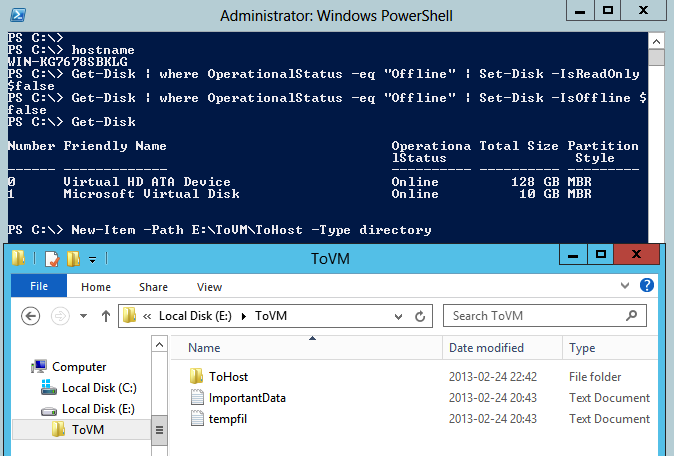
And here you can see what happens if I move from a folder that is not named after the VM´s name

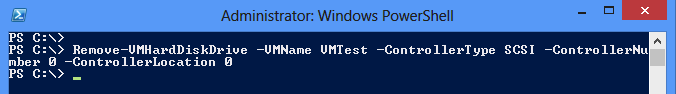
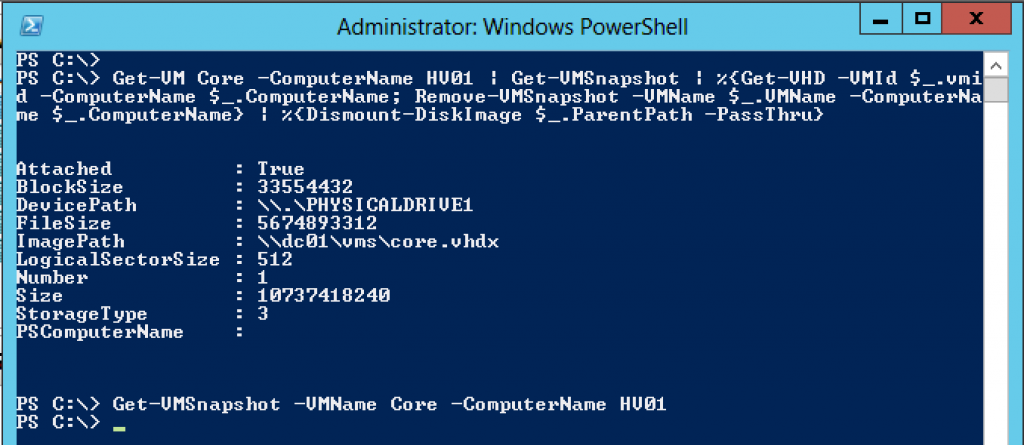
And here is a screendump of the folders that are left in the c:\vms that you need to manually delete and you might want to check that not another vm is residing inside these folders before removing them 😛
<#
.Synopsis
An updated Move-VMStorage function
.DESCRIPTION
To also remove the folder where the VM was residing this function also deletes the folder after moving the VM
This function also helps you in creating a folder in the path if forgotten
.EXAMPLE
Move-VMStorage2 -VMName test -ComputerName HV02 -Path \\SMB-srv01\VMs\test
.NOTES
Author: Niklas Akerlund 20130226
Version: 0.2
#>
function Move-VMStorage2
{
[CmdletBinding()]
[OutputType([int])]
Param
(
# A name of a VM
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$true,
Position=0)]
$VMName,
# The name of the Hyper-V host
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$true,
Position=1)]
$ComputerName = "localhost",
# The path where the VM is going to be relocated to.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=$true,
Position=2)]
[string] $Path
)
# Lets move and tidy the source folder
$VM = Get-VM $VMName -ComputerName $ComputerName
# For some reason the path does not get refreshed when moving one VM several times in the same console that is why i do a select *
$VMOldPath = Get-VM $VMName -ComputerName $ComputerName | select * -ExpandProperty Path
if ($Path -notmatch $VM.VMName){
$Path = $Path + "\" + $VM.VMName
Move-VMStorage -VM $VM -DestinationStoragePath $Path
}else{
Move-VMStorage -VM $VM -DestinationStoragePath $Path
}
if (($VMOldPath.StartsWith("\\")) -and $VMOldPath -match $VM.VMName) {
Remove-Item -Path $VMOldPath -Recurse -Force
}elseif ($VMOldPath -match $VM.VMName){
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $VM.ComputerName -ScriptBlock {Remove-Item -Path $Using:VMOldPath -Recurse -Force}
}else{
Write-Host "The VM :" $VM.VMName " was in the following path " $VMOldPath " Clean it manually!"
}
}