Adding 2016 DHCP Scopes with PowerShell in Windows 2012
I have had a lot to do and that is why I have not done so much updating on the blog, soon my third article will be published on Petri IT Knowledge 🙂 I have also attended the MMS in Las Vegas where I got loads of good information and meet lots of people!
In this post I want to show you the improvements in Windows 2012 and with the PowerShell native cmdlets in this version.
The task was to automatically create 2016 DHCP Scopes for clients on a DCHP server and every scope was a /29 net with 3 lease addresses and one router for each.
I tested this on a Windows 2008 R2 with the community powershell module and with the following script it took, and I am not kidding, almost 5 hours!! the module utilise the net sh commands with dhcp and probably there could be a lot of improvements for performance, and seriously, just creating one or two scopes can be done in the gui but doing over 2000 will demand a scripted way!
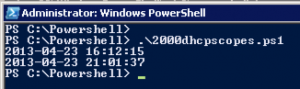
# Massive DHCP Scope 2016
#
# Niklas Akerlund 2013-04-24
write-host (get-date)
for($b=1;$b -le 63 ; $b++){
for($i=0;$i -le 255){
New-DHCPScope -Server localhost -Name 10.10.$b.$i -Address 10.10.$b.$i -SubnetMask 255.255.255.248 | Out-Null
$startip = $i+2
$endip = $i+4
$router = $i+1
Add-DHCPIPRange -Server localhost -Scope 10.10.$b.$i -StartAddress 10.10.$b.$startip -EndAddress 10.10.$b.$endip | Out-Null
Get-DHCPScope -Server localhost -Scope 10.10.$b.$i | Set-DHCPOption -OptionID 003 -DataType IPADDRESS -Value 10.10.$b.$router | Out-Null
$i = $i +8
}
}
write-host (get-date)
With the PowerShell DHCP module for WIndows 2012 I have created the following script for creating the same amount of scopes and configuration and running it took only about 1 minute!!
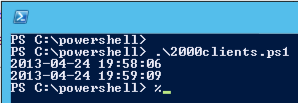
# Massive DHCP Scope 2016
#
# Niklas Akerlund 2013-04-24
write-host (get-date)
for($b=1;$b -le 63 ; $b++){
for($i=0;$i -le 255){
$startip = $i+2
$endip = $i+4
$router = $i+1
Add-DhcpServerv4Scope -Name 10.10.$b.$i -StartRange 10.10.$b.$startip -EndRange 10.10.$b.$endip -SubnetMask 255.255.255.248
Set-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -ScopeId 10.10.$b.$i -Router 10.10.$b.$router
$i = $i +8
}
}
write-host (get-date)
As you can see, handling lots of changes and configurations can easily be done in the new Windows 2012 and it´s native cmdlets!