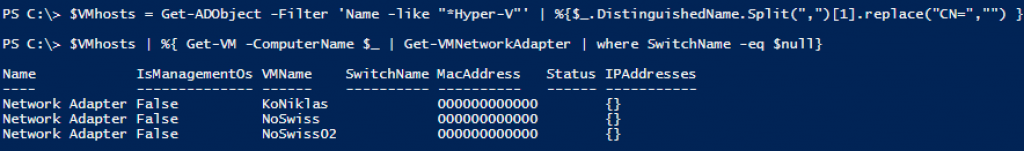
Managing Hyper-V 2012 with Win 2008 R2/7 RSAT tools
I have noticed several forum posts about some issues managing the Windows 2012 Hyper-V or the free Hyper-V 2012 Server.
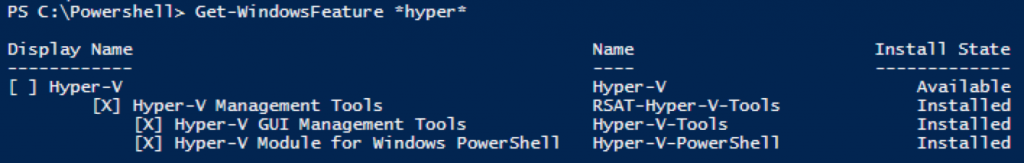
Most of the cases are because people try to use the Hyper-V manager in Windows 2008 R2 or the Hyper-V manager from the RSAT tools in Windows 7.
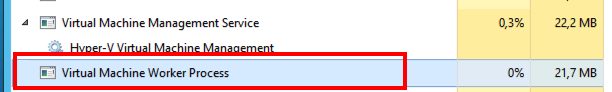
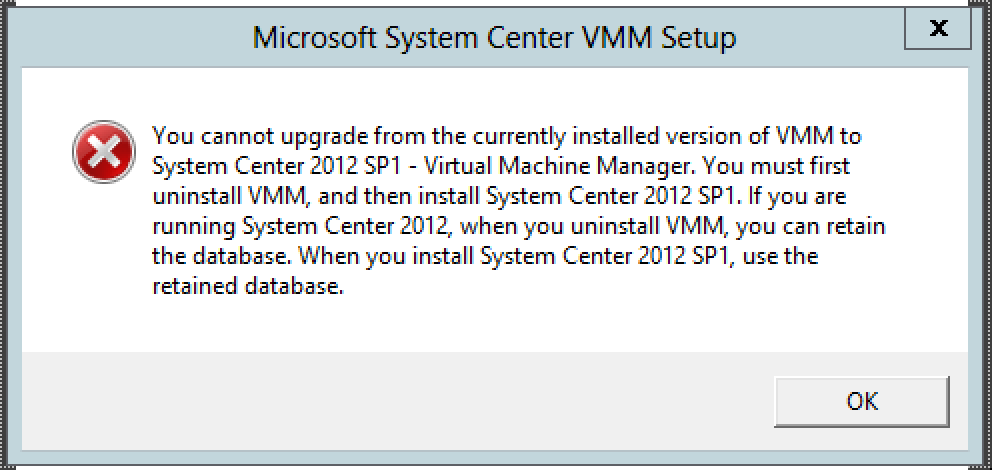
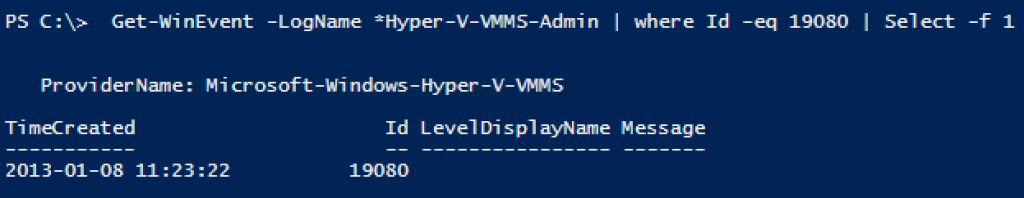
As you can see on this screendump, you can successfully connect to a 2012 Hyper-V from a Win7 Hyper-V manager. But the features offered in the new Hyper-V is not accessible in this GUI, this causes some confusion when handling the VM´s and the Hyper-V role!
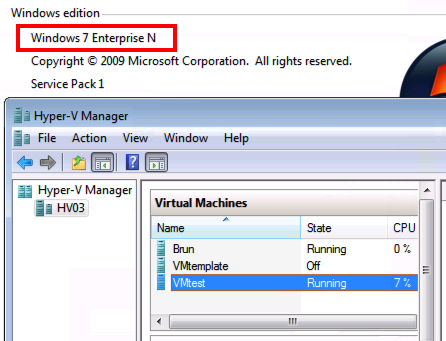
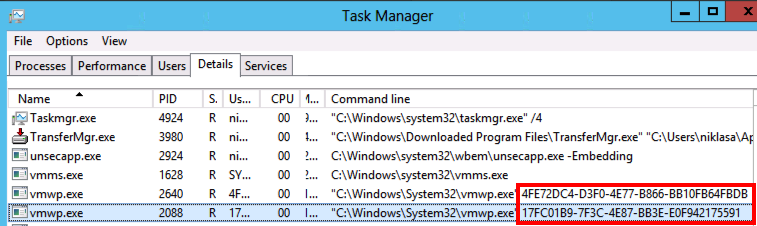
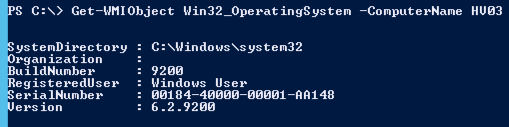
And here you can see that the server HV03 really is a 2012 version:
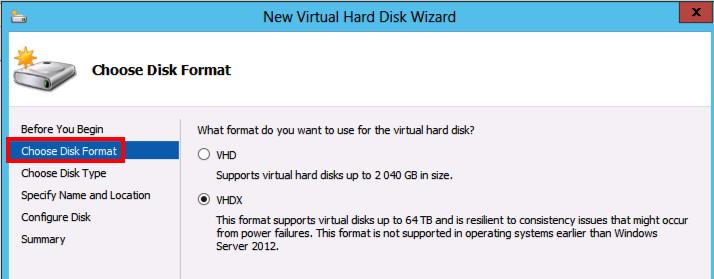
So for example, when you are going to edit the VM and add a new virtual harddisk you will notice that the new VHDX is not available
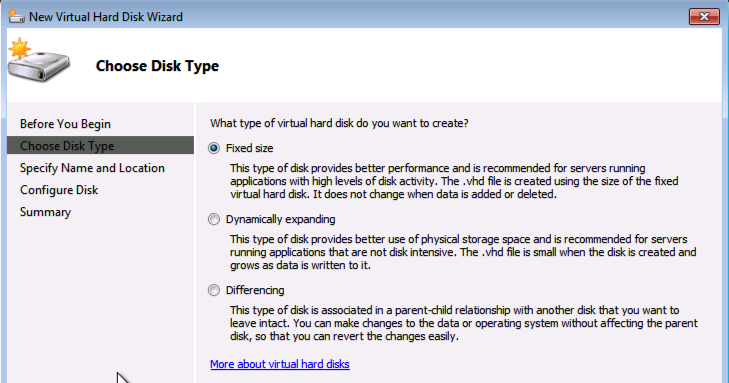
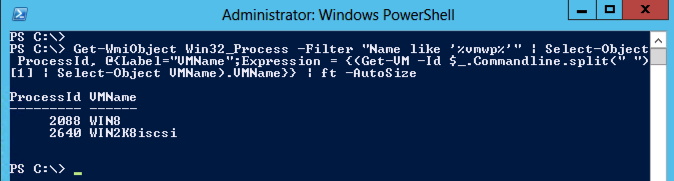
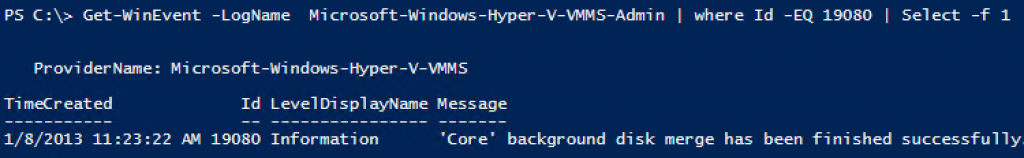
And as you can see in the following screendump from a new Hyper-V manager:
Some things work though, you can set more memory than the Windows 2008 R2 limit and also set more than 4 vCPU´s!
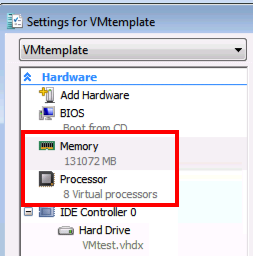
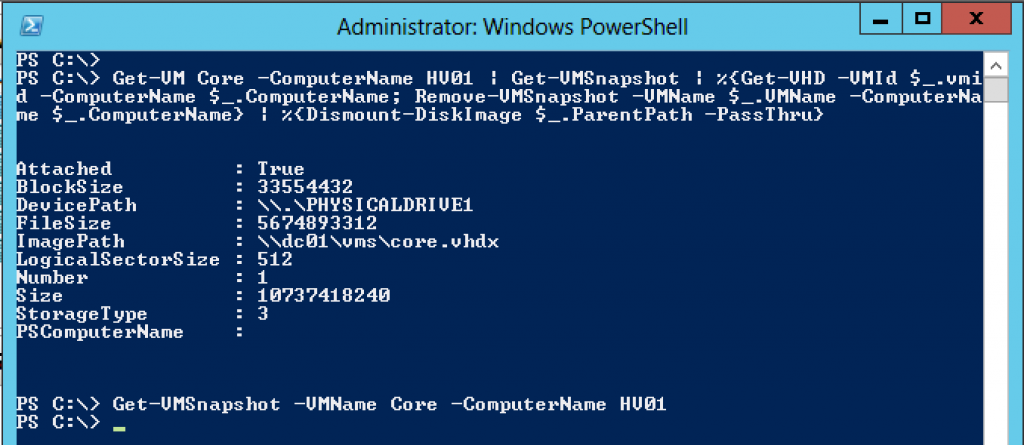
The ability to setup Hyper-V replica and to move VM´s are absent from the GUI as these are new features.
Yes It works to manage some stuff in the old Hyper-V manager but not all so my recommendation as it is not supported you should install a Windows 2012 or a Windows 8 to manage your new Hyper-V 2012 and also more importanly you will get the powershell module to manage it!
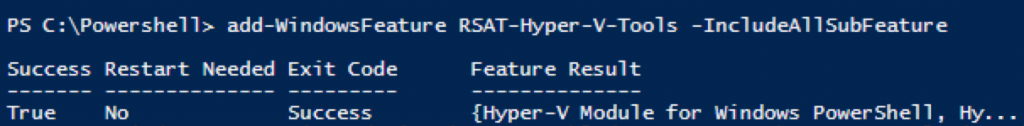
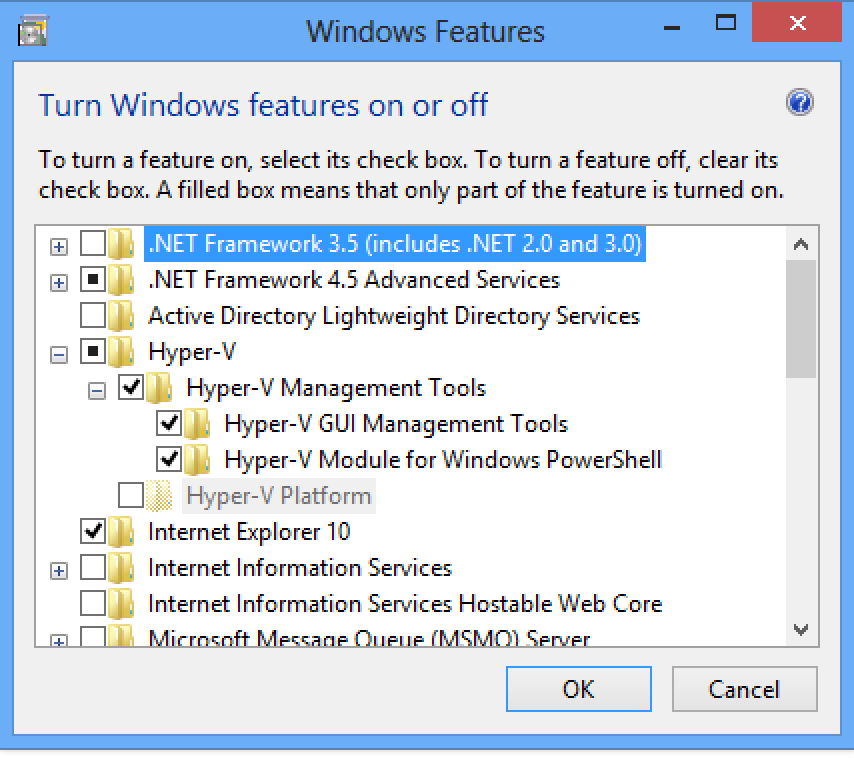
I have made a blog post about how to enable the Hyper-V manager and the Powershell module on the Windows 2012 and Windows 8!